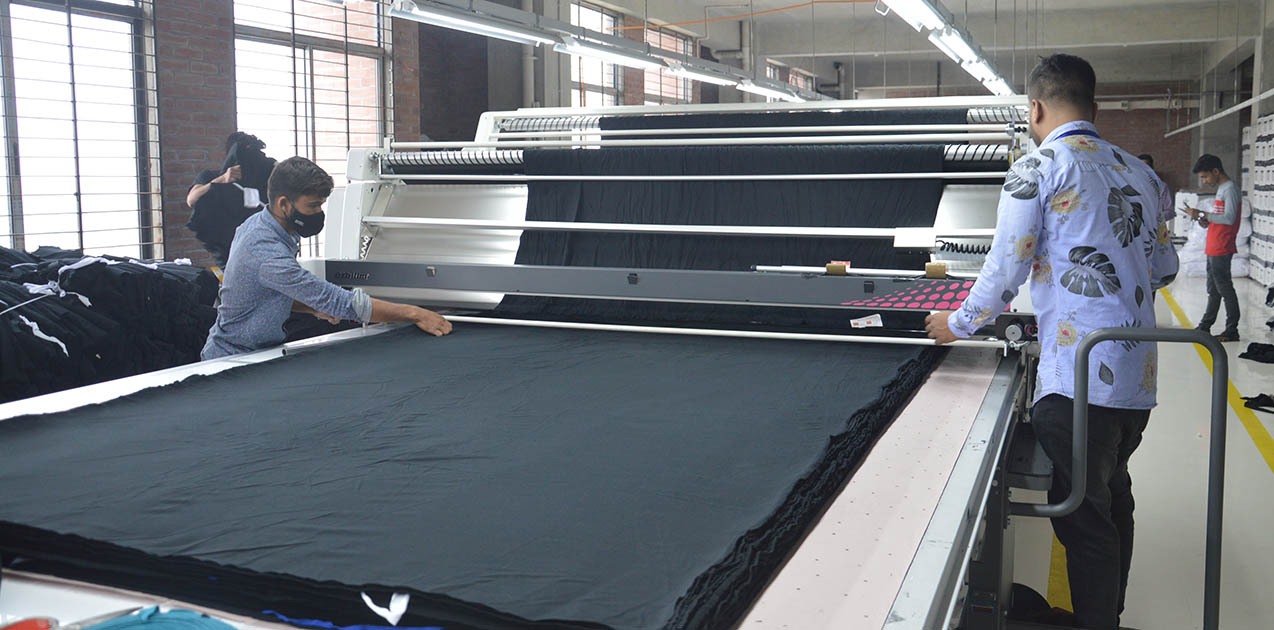
Quality fabric
We are help for selecting Good quality of fabric materials using Different Different
catlouages .
The type of fiber used in the fabric significantly influences its characteristics.
Natural fibers like cotton, silk, wool, and linen are known for their breathability
and comfort. Synthetic fibers like polyester and nylon can provide durability and
resistance to wrinkles.
Consider the weight of the fabric, which is measured in grams per square meter (GSM)
or ounces per square yard. The weight affects the drape and thickness of the
fabric. Lighter fabrics are suitable for warm weather, while heavier fabrics may be
more appropriate for cooler climates.
The weave or knit structure of the fabric determines its texture, appearance, and
stretch. Common weaves include plain, twill, and satin, while knits include jersey,
rib, and interlock. Choose a weave or knit that complements the garment's design and
desired characteristics.
Considering the durability of the fabric, especially if the cloth will be subject to
frequent wear and washing. Durability is influenced by factors such as fiber
strength, weave or knit construction, and overall fabric quality.